How to perform a MIL-STD-461 CS109, Conducted susceptibility, structure current test[edit]
This application note explains how the MIL-STD-461 CS109, Conducted susceptibility, structure current test can be performed with RadiMation®
The exact requirements and test methods for the CS109 are specified in the MIL-STD-461.
Necessary equipment[edit]
The following devices are necessary to perform the CS109 test:
- Signal generator
- Amplifier
- Coupling Transformer
- Current sensor
- Cable drivers with corrections
- Sensor power meter / Analyser
- 0.5 Ohm resistor
- Isolation Transformer

|
Note:
|
If the current unit is shown as μA, it can be changed to dBμA by clicking Units, select Current and click Edit to change this.
|
Define the test level[edit]
Create a correction file for the test level[edit]
-
 File
File
-
 New
New
-
 Correction
Correction
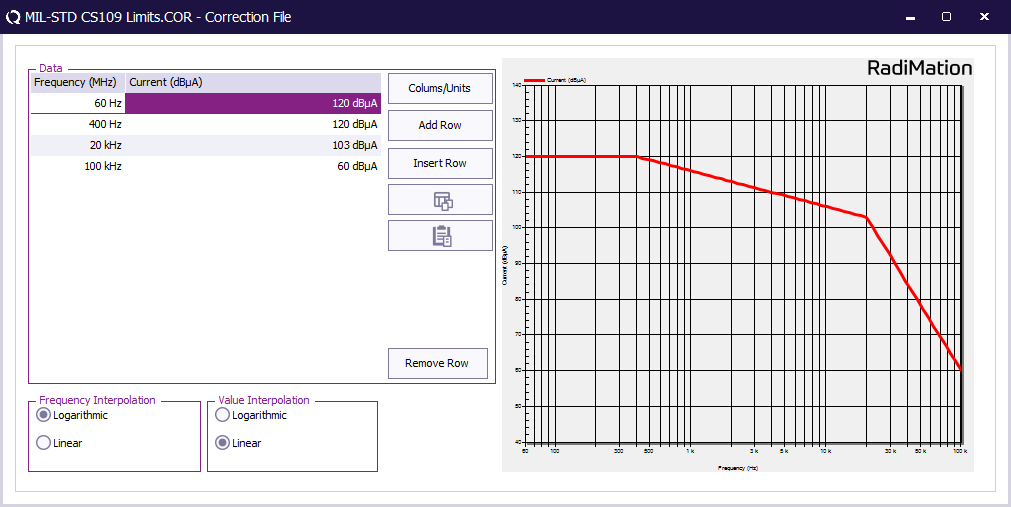
First create a correction file in RadiMation® and specify the test level (See 'FIGURE CS109-1. CS109 limit.').
Ensure that the correction file has a Frequency column and a Current column with the unit set to dBμA.
-
 File
File
-
 Save correction
Save correction
Store the test level as correction file on disk.
This correction file with the test level will be used during EUT testing.
EUT Testing[edit]
EUT Testing equipment[edit]
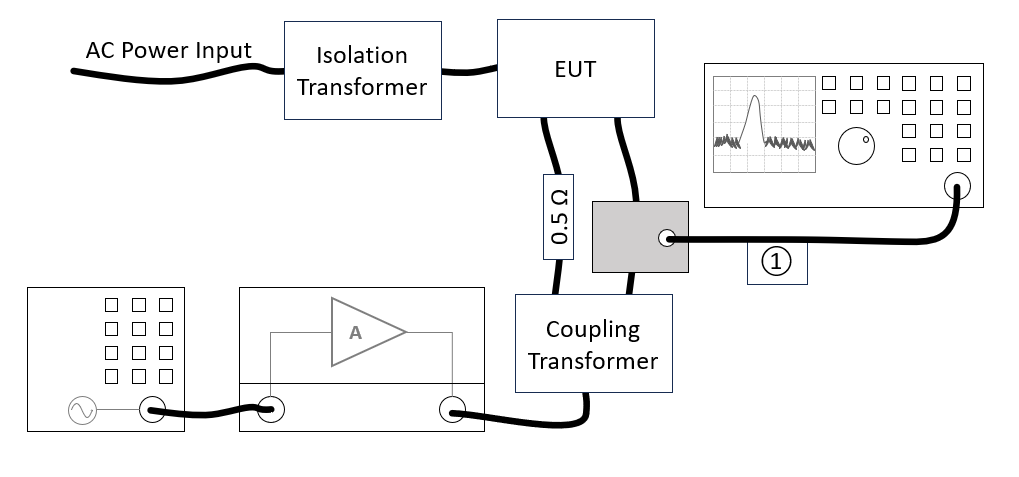
The configuration of the eut test site should contain the following devices:
| # |
Device name |
Tab in testsite configuration window |
note
|
|
Signal Generator |
Devices 1 |
The signal generator to use
|
|
Amplifier |
Devices 1 |
The amplifier to use
|
|
Sensor powermeter |
Devices 2 |
The power meter or analyser to use for measuring the current
|
|
Current Sensor |
Devices 2 |
The current sensor to use with transfer factor attached to the driver
|
|
Injection device |
Devices 2 |
The injection device to use
|
| Cables
|
| ① |
Cable current -> power meter |
Cables |
Cable with a correction file specified for the cable loss
|
Configure the EUT test[edit]
To perform the test on the EUT, create a conducted immunity multiband test.
The conducted immunity multiband test, can be started by selecting from the menu:
-
 Tests
Tests
-
 Conducted Immunity
Conducted Immunity
-
 Multiband
Multiband
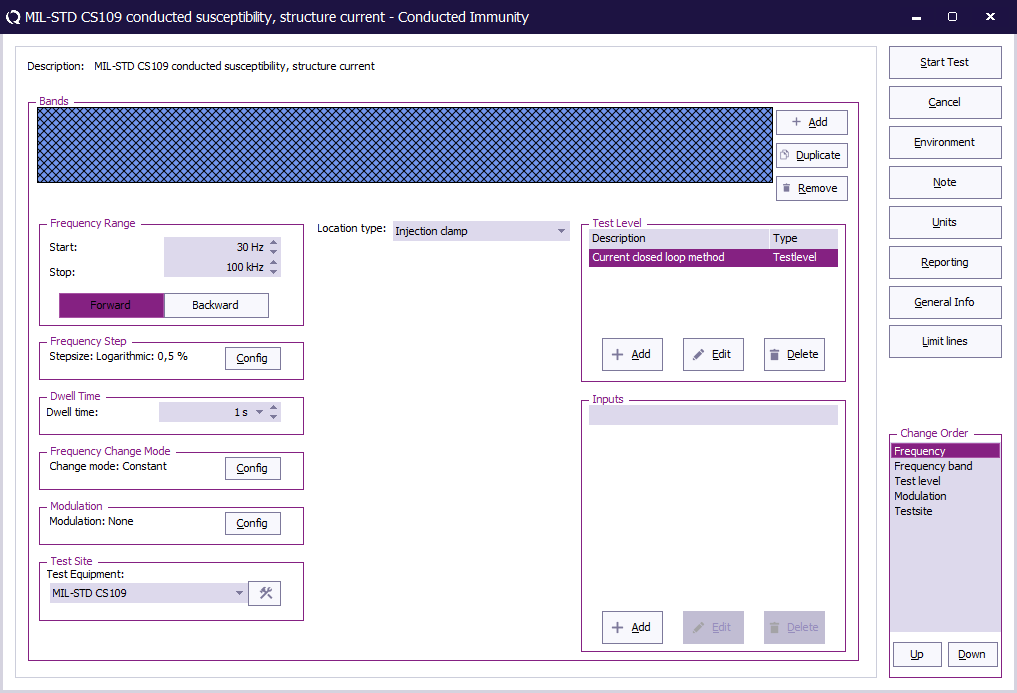
 Start Start
|
The start frequency of the test. For example 30 Hz.
|
 End End
|
The stop frequency of the test. For example 100 kHz.
|
 Frequency Step Frequency Step
|
The frequency step, see Table III.
|
 Dwell Time Dwell Time
|
The dwell time.
|
 Frequency Change Mode Frequency Change Mode
|
Constant.
|
 Modulation Modulation
|
CS109 does not specify a modulation to use.
|
 Test equipment Test equipment
|
The equipment needed for the conducted immunity test.
|
 Location Type Location Type
|
Injection clamp.
|
 Test Level Test Level
|
Specify the current substitution method. Also add a "Measured Current Limit"
|
 Inputs Inputs
|
No inputs are needed.
|
At TestLevel click Add to add a new Test level and select TestLevel - Current closed loop method
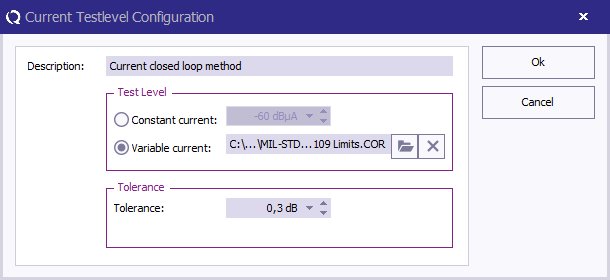
 Description Description
|
The description of the test level.
|
 Test level Test level
|
Variable current, and specify the correction file for the applicable test level.
|
 Tolerance Tolerance
|
Specify the tolerance to use.
|
When all settings are configured press Start Test to run the test.
EUT Test Result[edit]
Once the test is finished, the results of this test are stored in the EUT file and available as one of the performed Tests in the EUT file. Selecting the corresponding test result and pressing on Info will show the test results again.
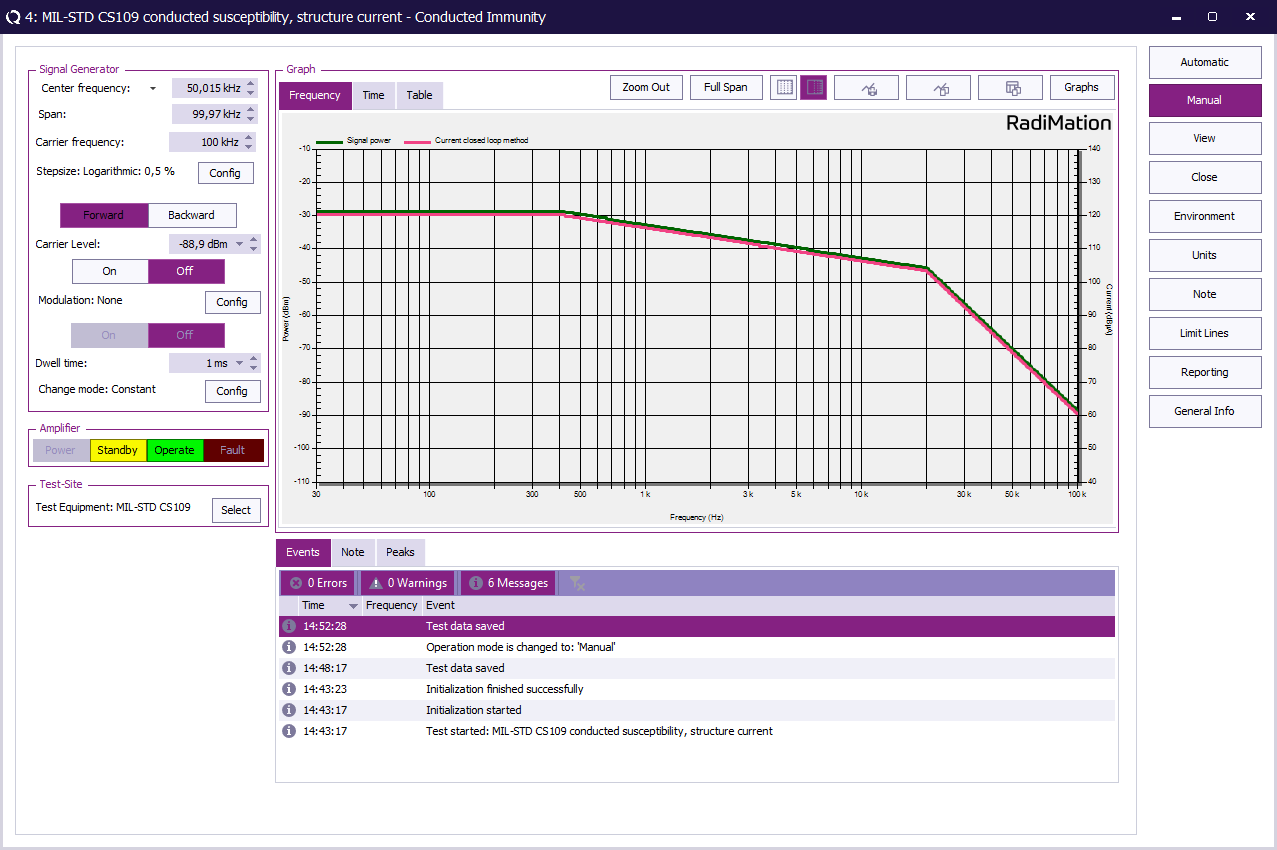
Conclusion[edit]
The RadiMation® Conducted Immunity multiband test can be used to perform the CS109 test with a current closed loop method test level and a variable test level specified in a correction file.
 File
File
 New
New
 Correction
Correction  File
File
 Save correction
Save correction  Tests
Tests
 Conducted Immunity
Conducted Immunity
 Multiband
Multiband 



