Rohde & Schwarz ESI/ESIB/ESCI/ESPI Controlled LISN: Difference between revisions
(Initial DeviceDriverInfo page creation) |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{DeviceDriverInfo | {{DeviceDriverInfo | ||
|DLLFile=RADBCI.DLL | |DLLFile=RADBCI.DLL | ||
|DeviceBrand=Rohde & Schwarz | |DeviceBrand=Rohde & Schwarz | ||
|DeviceDriverName=RSLISNUSERPORT_ESI | |||
|DeviceType=ESI/ESIB/ESCI/ESPI Controlled LISN | |||
|SupportedDeviceTypes=1024 | |SupportedDeviceTypes=1024 | ||
| | |HideAutoData=1 | ||
}} | }} | ||
The [[Rohde & Schwarz ESI/ESIB/ESCI/ESPI Controlled LISN]] device driver can be used to automatically control LISNs that are connected a R&S ESI-series analyzer. | |||
Instead of controlling the LISN itself, {{RadiMation}} will connect to the R&S analyzer. The R&S analyzer is connected to the LISN, by using a cable between the userport of the R&S analyzer and the LISN itself. The definition of the cable, and how it should be connected is very often described in the manual of the LISN itsef. When another line of the LISN should be selected, {{RadiMation}} will send the correct command to the R&S Analyzer, which will activate the correct outputs on the userport of the R&S Analyzer. | |||
This device driver is no only working for the R&S ESI, but also for all the other related [[Rohde & Schwarz]] analyzers from the same series. Thus also the LISN that is connected to a [[Rohde & Schwarz ESPI]] can be controlled by using this device driver. | |||
{{:DeviceDriverCommunicationTab}} | |||
{{:DeviceDriverFrequencyRangeTab}} | |||
== Example == | |||
For example see the documentation and explanation that is available for the Schwarzbeck NSLK 8128, when it is equipped with the '[http://www.schwarzbeck.de/en/lisn-line-impedance-stabilisation-networks/v-lisn-en/v-lisn-cispr-16-1-2/305-nslk-8128.html NSLK 8128 Opt. RC]'. | |||
Latest revision as of 11:42, 12 June 2020
The Rohde & Schwarz ESI/ESIB/ESCI/ESPI Controlled LISN device driver is a LISN which is supported by RadiMation®.
Configuration[edit]
The following tabs are available in the advanced configuration of the Rohde & Schwarz ESI/ESIB/ESCI/ESPI Controlled LISN:
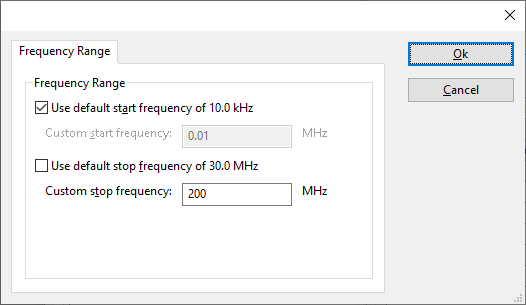
The frequency range of the Rohde & Schwarz ESI/ESIB/ESCI/ESPI Controlled LISN as provided by the manufacturer is shown and selected as default. It is possible to overrule these frequencies and to manual adjust the allowed frequency range of the Rohde & Schwarz ESI/ESIB/ESCI/ESPI Controlled LISN.
| If the checkbox is checked, the default start frequency will be used as the lowest usable frequency in a test for this device. |
| If the Use default start frequency checkbox is unchecked, another start frequency (expressed in MHz) can be specified. The customized start frequency will then be used as the lowest usable frequency in a test for this device. The customized frequency can be a limitation or an extension of the default start frequency. |
| If the checkbox is checked, the default stop frequency will be used as the highest usable frequency in a test for this device. |
| If the Use default stop frequency checkbox is unchecked, another stop frequency (expressed in MHz) can be specified. The customized stop frequency will then be used as the highest usable frequency in a test for this device. The customized frequency can be a limitation or an extension of the default stop frequency. |
Specifying a different frequency range can be useful if for example:
- A device (like a coupler, antenna, injection device, cable, etc...) is still useable (but out of specification) outside the standard suggested frequency range.
- An external mixer is used to measure an extended frequency range.
- An up- or down-convertor is used to shift the frequency range.
- A newer model of a device is present that has an extended frequency range, and still uses the same remote control commands.
Be careful changing these setting as RadiMation® is no longer able to verify if the Rohde & Schwarz ESI/ESIB/ESCI/ESPI Controlled LISN is used outside frequency range that is specified by the manufacturer. This may result to serious damage of your measurement device.
The Rohde & Schwarz ESI/ESIB/ESCI/ESPI Controlled LISN device driver can be used to automatically control LISNs that are connected a R&S ESI-series analyzer.
Instead of controlling the LISN itself, RadiMation® will connect to the R&S analyzer. The R&S analyzer is connected to the LISN, by using a cable between the userport of the R&S analyzer and the LISN itself. The definition of the cable, and how it should be connected is very often described in the manual of the LISN itsef. When another line of the LISN should be selected, RadiMation® will send the correct command to the R&S Analyzer, which will activate the correct outputs on the userport of the R&S Analyzer.
This device driver is no only working for the R&S ESI, but also for all the other related Rohde & Schwarz analyzers from the same series. Thus also the LISN that is connected to a Rohde & Schwarz ESPI can be controlled by using this device driver.
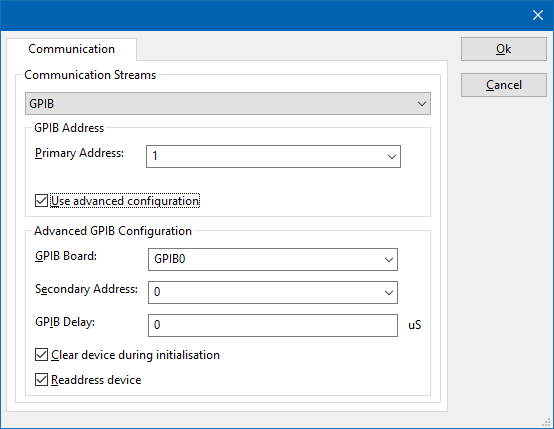
On the Communication tab, the desired communication method can be selected and configured. Depending on the selected method, additional relevant settings are shown and can be configured.
| Selects the medium or method that should be used to communicate with the device. Depending on the capabilities of the device this can be one or more of:
See the Communication Settings in Chapter 15, on how to configure each of these methods. |
The frequency range of the Rohde & Schwarz ESI/ESIB/ESCI/ESPI Controlled LISN as provided by the manufacturer is shown and selected as default. It is possible to overrule these frequencies and to manual adjust the allowed frequency range of the Rohde & Schwarz ESI/ESIB/ESCI/ESPI Controlled LISN.
| If the checkbox is checked, the default start frequency will be used as the lowest usable frequency in a test for this device. |
| If the Use default start frequency checkbox is unchecked, another start frequency (expressed in MHz) can be specified. The customized start frequency will then be used as the lowest usable frequency in a test for this device. The customized frequency can be a limitation or an extension of the default start frequency. |
| If the checkbox is checked, the default stop frequency will be used as the highest usable frequency in a test for this device. |
| If the Use default stop frequency checkbox is unchecked, another stop frequency (expressed in MHz) can be specified. The customized stop frequency will then be used as the highest usable frequency in a test for this device. The customized frequency can be a limitation or an extension of the default stop frequency. |
Specifying a different frequency range can be useful if for example:
- A device (like a coupler, antenna, injection device, cable, etc...) is still useable (but out of specification) outside the standard suggested frequency range.
- An external mixer is used to measure an extended frequency range.
- An up- or down-convertor is used to shift the frequency range.
- A newer model of a device is present that has an extended frequency range, and still uses the same remote control commands.
Be careful changing these setting as RadiMation® is no longer able to verify if the Rohde & Schwarz ESI/ESIB/ESCI/ESPI Controlled LISN is used outside frequency range that is specified by the manufacturer. This may result to serious damage of your measurement device.
Example[edit]
For example see the documentation and explanation that is available for the Schwarzbeck NSLK 8128, when it is equipped with the 'NSLK 8128 Opt. RC'.