RadiMation Application Note 165: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Created page with "__NOTOC__ == How to perform a IEC 61000-4-6, Conducted immunity test == This application note explains how the IEC 61000-4-6 conducted immunity test can be performed with {{RadiMation}}. The IEC 61000-4-6 conducted immunity test method is used for electrical and electronic equipment that may be subjected to radio-frequency disturbances conducted along cables coming from radio transmitters in the frequency range from 150 kHz up to 80 MHz. The exact requirements, calibrati...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
== How to perform | == How to perform an IEC 61000-4-6, Conducted immunity test == | ||
This application note explains how the IEC 61000-4-6 conducted immunity test can be performed with {{RadiMation}}. | This application note explains how the IEC 61000-4-6 conducted immunity test can be performed with {{RadiMation}}. | ||
The IEC 61000-4-6 conducted immunity test method is used for electrical and electronic equipment that may be subjected to radio-frequency disturbances conducted along cables coming from radio transmitters in the frequency range from 150 kHz up to 80 MHz. The exact requirements, calibration and EUT test methods are described in the IEC 61000-4-6 standard. | The IEC 61000-4-6 conducted immunity test method is used for electrical and electronic equipment that may be subjected to radio-frequency disturbances conducted along cables coming from radio transmitters in the frequency range from 150 kHz up to 80 MHz. The exact requirements, calibration and EUT test methods are described in the IEC 61000-4-6 standard. | ||
Revision as of 13:52, 9 September 2025
How to perform an IEC 61000-4-6, Conducted immunity test[edit]
This application note explains how the IEC 61000-4-6 conducted immunity test can be performed with RadiMation®. The IEC 61000-4-6 conducted immunity test method is used for electrical and electronic equipment that may be subjected to radio-frequency disturbances conducted along cables coming from radio transmitters in the frequency range from 150 kHz up to 80 MHz. The exact requirements, calibration and EUT test methods are described in the IEC 61000-4-6 standard.
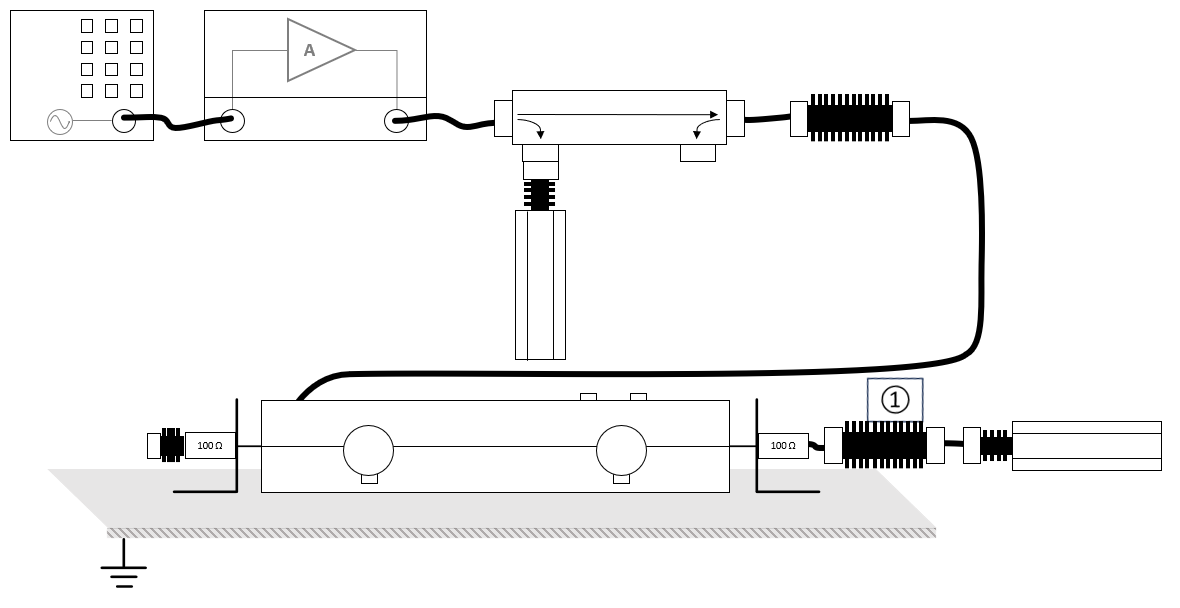
Necessary equipment[edit]
- Signal generator
- Amplifier
- Coupler
- Forward power meter
- Injection device
- Calibration jig
- Attenuator (optional)
- Sensor power meter
Calibration procedure[edit]
The calibration is performed to determine the power required to match the corresponding voltage test level seen at the output of the injection device.
The configuration of the calibration test site should contain the following devices:
| # | Device name | Tab in testsite configuration window | note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Generator | Devices 1 | The signal generator to use | |
| Amplifier | Devices 1 | The amplifier to use | |
| Coupler | Devices 1 | Coupler | |
| Forward power meter | Devices 1 | Forward power meter | |
| Injection device | Devices 2 | The injection clamp or CDN | |
| Calibration Jig | Devices 2 | The calibration jig to use | |
| Sensor power meter | Devices 2 | Power meter | |
| Cables | |||
| ① | Cable current -> power meter | Cables | Cable with the specified loss of the used attenuator |