How to perform an IEC 61000-4-6, Conducted immunity test[edit]
This application note explains how the IEC 61000-4-6 conducted immunity test can be performed with RadiMation®.
The IEC 61000-4-6 conducted immunity test method is used for electrical and electronic equipment that may be subjected to radio-frequency disturbances conducted along cables coming from radio transmitters in the frequency range from 150 kHz up to 80 MHz. The exact requirements, calibration and EUT test methods are described in the IEC 61000-4-6 standard.
Necessary equipment[edit]
- Signal generator
- Amplifier
- Coupler
- Forward power meter
- Injection device
- Calibration jig with 100 Ohm resistors
- 50 Ohm load
- Attenuator in front of sensor power meter (optional)
- Sensor power meter
Calibration procedure[edit]
The calibration is performed to determine the power required to match the corresponding voltage test level seen at the output of the injection device.
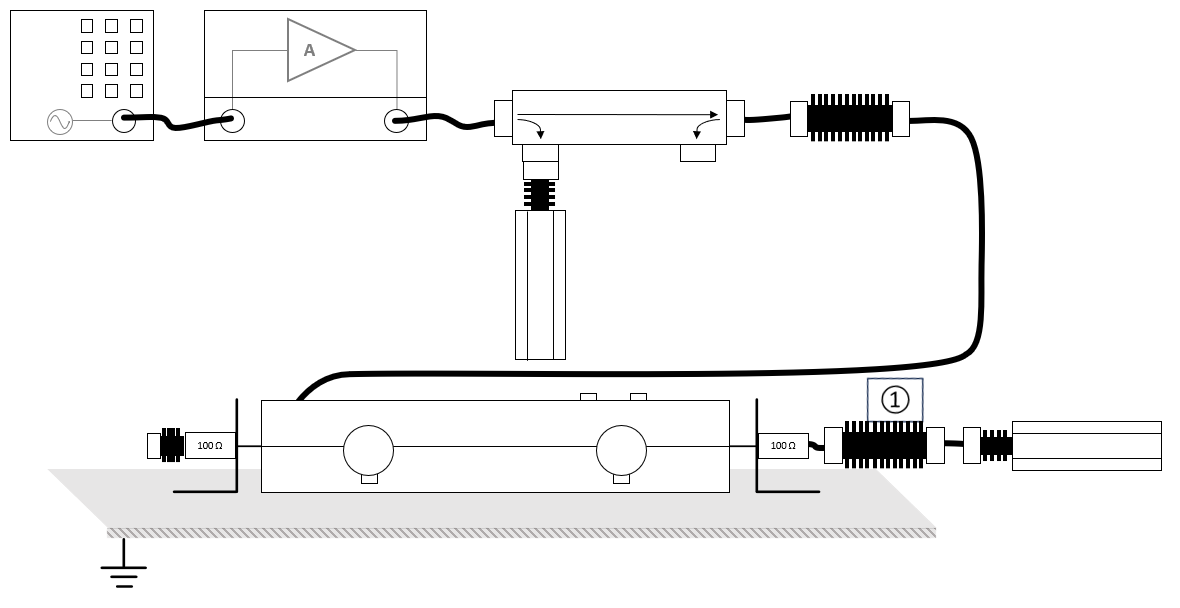
The configuration of the calibration test site should contain the following devices:
| # |
Device name |
Tab in testsite configuration window |
note
|
|
Signal Generator |
Devices 1 |
The signal generator to use
|
|
Amplifier |
Devices 1 |
The amplifier to use
|
|
Coupler |
Devices 1 |
Coupler
|
|
Forward power meter |
Devices 1 |
Forward power meter
|
|
Injection device |
Devices 2 |
The injection clamp or CDN
|
|
Calibration Jig |
Devices 2 |
The calibration jig to use
|
|
Sensor power meter |
Devices 2 |
Power meter
|
| Cables
|
| ① |
Cable current -> power meter |
Cables |
Cable with the specified loss of the used attenuator
|
Optional Attenuator[edit]
Before deciding whether an attenuator is required in front of the sensor power meter, the power level at the output of the calibration jig must be calculated first.
Why a factor of 6 applies[edit]
Two effects reduce the test voltage before it appears at the 50 Ω measurement port:
- Impedance conversion (150 Ω → 50 Ω): factor of 3
- Open-circuit to loaded conversion: factor of 2
Combined, this gives a total factor of 6:

Conversion from test level (dBµV) to jig output (dBµV)[edit]


Conversion to power in dBm[edit]

Short form[edit]
By combining the steps:

Examples[edit]
The following table shows the results for common test levels:
| Test Level (V, rms) |
Test Level (dBµV) |
Jig Output (dBµV) |
Power (dBm)
|
| 1 |
120.0 |
104.44 |
−2.56
|
| 3 |
129.54 |
113.98 |
+6.98
|
| 10 |
140.0 |
124.44 |
+17.44
|
Conclusion[edit]
Using the calculated power levels, it is straightforward to determine the amount of attenuation required for a given sensor power meter.
For example, the Raditeq RPR2006C has a specified measurement range up to +10 dBm.
- At 1 V and 3 V test levels (−2.56 dBm and +6.98 dBm), no attenuation is required.
- At 10 V test level (+17.44 dBm), the input exceeds the safe range by approximately 7.5 dB.
In this case, adding at least a 10 dB attenuator ensures the sensor operates within its specified limits. Make sure to correct for this 10 dB by creating a cable device driver with a correction file attached to it, then configure this cable in the test site: Cables, Cable current -> power meter.
Configure the injection device and jig device driver[edit]
In order for RadiMation to calibrate on the correct test level, the injection device and jig device driver must be configured correctly.
Jig device driver[edit]
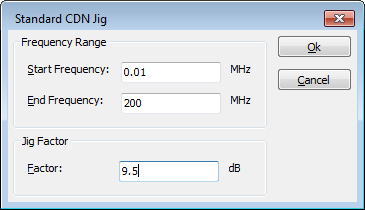
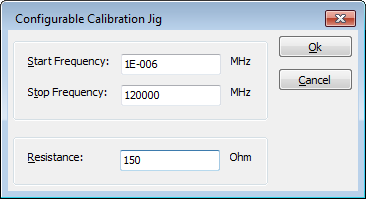
For a 150 Ω system the resistance is 150 Ω or uses a jig factor of 9.5 dB.
Injection device driver[edit]
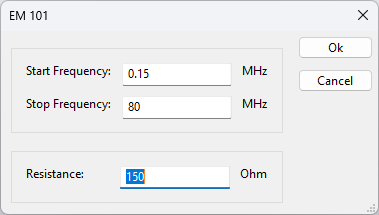
For the injection device driver the impedance should also be set to 150 Ω if that is configurable.
Configure the calibration[edit]
The calibration can be configured and started from the menu by selecting:
-
 Calibration
Calibration
-
 System calibration
System calibration
-
 Conducted immunity
Conducted immunity
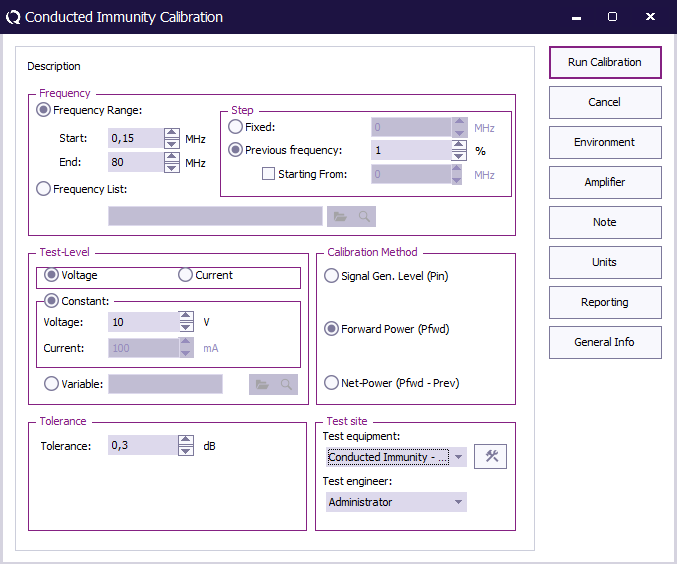
 Start Start
|
The start frequency of the calibration. For example 150 kHz.
|
 End End
|
The stop frequency of the calibration. For example 80 MHz.
|
 Step Step
|
The frequency step, in this case 1%.
|
 Test level Test level
|
The test level, in this case Voltage.
|
 Voltage Voltage
|
The voltage test level, 1 V, 3 V or 10 V.
|
 Tolerance Tolerance
|
The regulation tolerance.
|
 Calibration method Calibration method
|
The power measurement that should be the result of the calibration: Forward power
|
 Test equipment Test equipment
|
Calibration test equipment.
|
 Test engineer Test engineer
|
The engineer that performed the calibration.
|
When the calibration has finished, RadiMation® will ask to store the calibration file.
EUT Test[edit]
EUT testing equipment[edit]
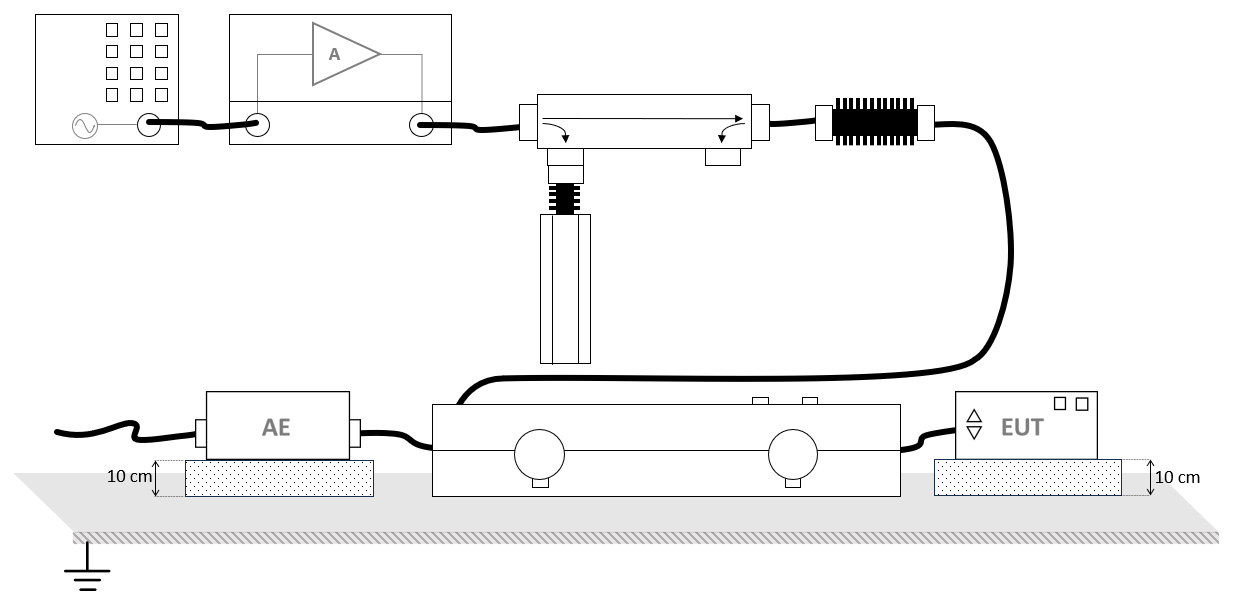
The configuration of the RadiMation® EUT test site should contain the following devices:
| # |
Device name |
Tab in testsite configuration window |
note
|
|
Signal Generator |
Devices 1 |
The signal generator to use
|
|
Amplifier |
Devices 1 |
The amplifier to use
|
|
Coupler |
Devices 1 |
The coupler to use
|
|
Forward power meter |
Devices 1 |
The forward power meter to use
|
|
Injection device |
Devices 2 |
The injection clamp or CDN to use
|
Configure the EUT test[edit]
To perform the actual test on the EUT, create a conducted immunity multiband test.
The conducted immunity multiband test configuration, can be opened by selecting from the menu:
-
 Tests
Tests
-
 Conducted Immunity
Conducted Immunity
-
 Multiband
Multiband
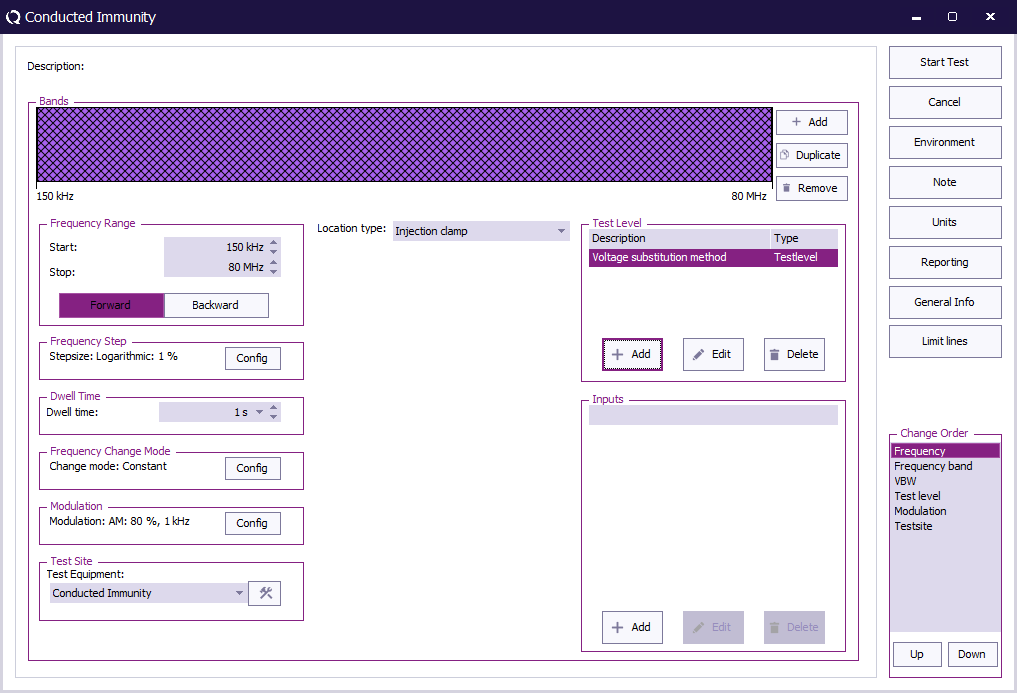
 Start Start
|
The start frequency of the test. For example 150 kHz.
|
 End End
|
The stop frequency of the test. For example 80 MHz.
|
 Frequency Step Frequency Step
|
The frequency step, 1%.
|
 Dwell Time Dwell Time
|
The dwell time.
|
 Frequency Change Mode Frequency Change Mode
|
The method that is used to change from one to the next frequency: Constant.
|
 Modulation Modulation
|
Configure Amplitude Modulation with 1 kHz and 80 % duty cycle.
|
 Test equipment Test equipment
|
The equipment needed for the conducted immunity test.
|
 Location Type Location Type
|
Injection clamp.
|
 Test Level Test Level
|
Specify the Voltage substition method
|
 Inputs Inputs
|
No inputs are needed, this is optional.
|
To configure the modulation settings click Config next to the modulation settings, click the AM tab, and enter the amplitude modulation settings.
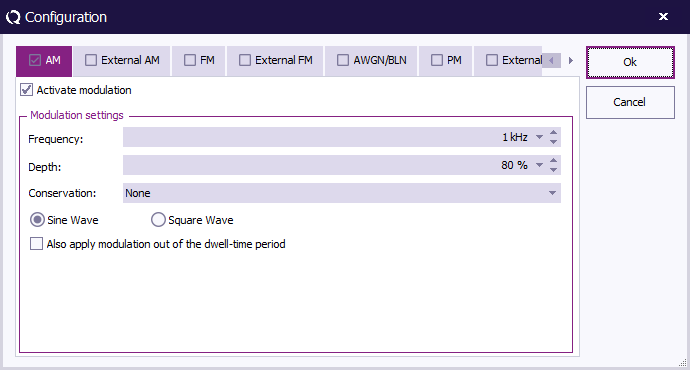
 Activate modulation Activate modulation
|
Check this checkbox to enable the amplitude modulation.
|
 Frequency Frequency
|
The AM frequency 1 kHz.
|
 Duty Cycle Duty Cycle
|
A depth of 80 %.
|
 Also apply modulation out of the dwell-time period Also apply modulation out of the dwell-time period
|
No need to apply modulation out of the dwell-time period.
|
At TestLevel click Add to add a new Test level and select TestLevel - Voltage substitution method
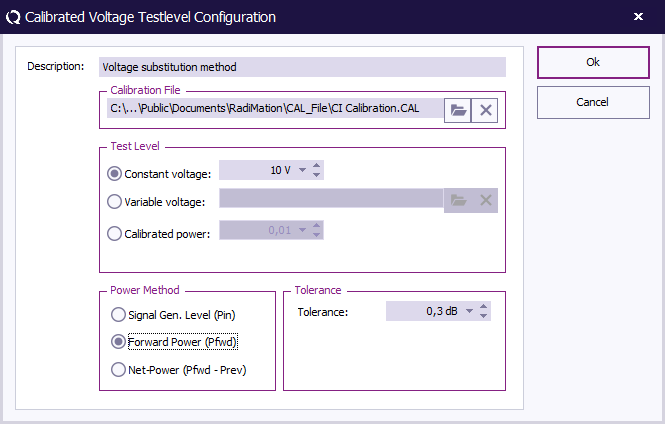
 Description Description
|
The description of the test level.
|
 Calibration file Calibration file
|
Select the calibration file created during the calibration procedure.
|
 Test level Test level
|
Constant voltage, 1 V, 3 V or 10 V.
|
 Calibration method Calibration method
|
Select Forward Power.
|
 Tolerance Tolerance
|
Specify the tolerance to use.
|
When all settings are configured press Start Test to run the EUT test.
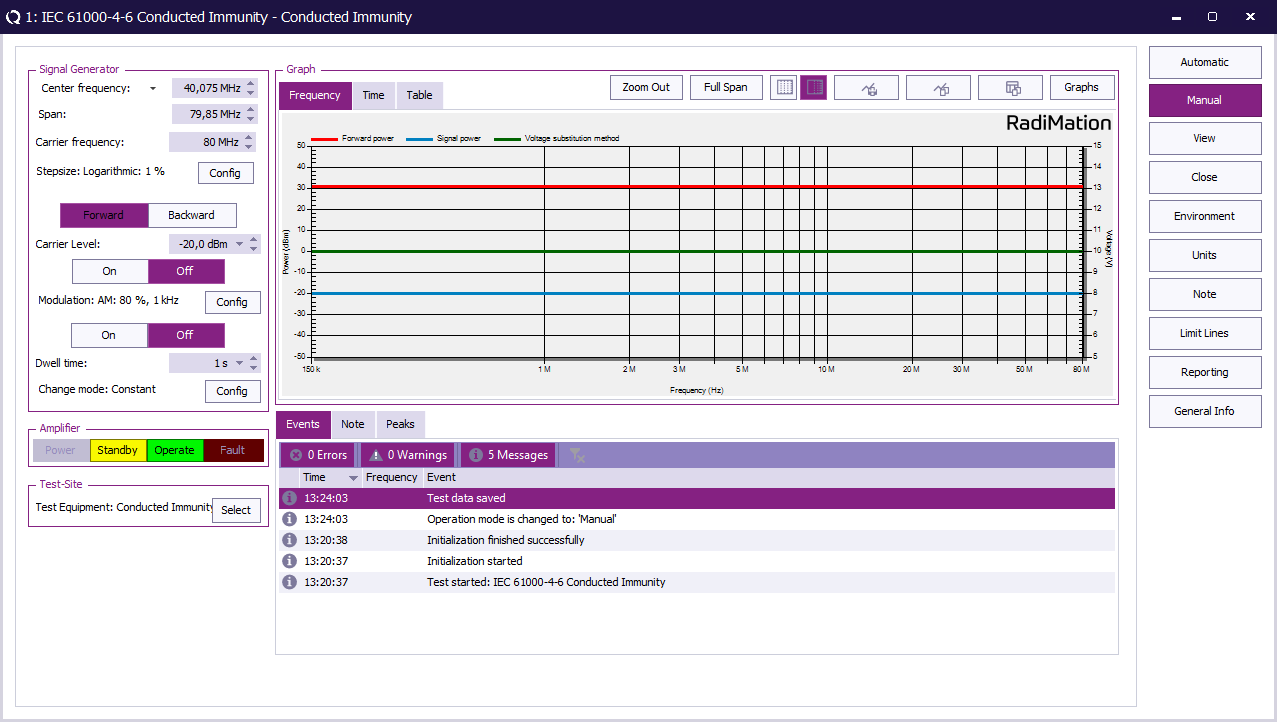
EUT test result[edit]
Once the test is finished, the results of this test are stored in the EUT file and available as one of the performed Tests in the EUT file. Selecting the corresponding test result and pressing on Info will show the test results again.
Conclusion[edit]
The IEC 61000-4-6 calibration can be performed by using the Conducted immunity calibration. The RadiMation® Conducted immunity multiband test can then be used to perform the IEC 61000-4-6 EUT test with a calibration file in the EUT test.
 Calibration
Calibration
 System calibration
System calibration
 Conducted immunity
Conducted immunity  Tests
Tests
 Conducted Immunity
Conducted Immunity
 Multiband
Multiband 













