Vector network analyser: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
==Sources== | ==Sources== | ||
(1)https://www.tek.com/vna/ttr500</br> | (1)https://www.tek.com/vna/ttr500 - Tektronix</br> | ||
(2)https://www.tek.com/document/primer/what-vector-network-analyzer-and-how-does-it-work | (2)https://www.tek.com/document/primer/what-vector-network-analyzer-and-how-does-it-work - Tektronix</br> | ||
Latest revision as of 15:56, 21 April 2020
Vector Network Analysers[edit]
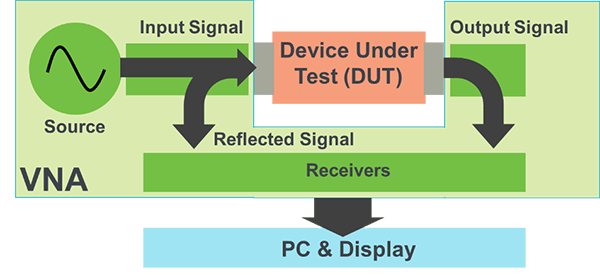
VNA's allow you to measure complex quantities such as reflection coefficients, impedance, admittance, return loss, insertion loss, gain, isolation of an DUT.
A VNA has both a source and a set of receivers used to determine changes to the stimulus caused by the DUT(1).
Types of measurement[edit]
Vector Network Analyzer’s perform two types of measurements – transmission and reflection.
Transmission measurements pass the Vector Network Analyzer stimulus signal through the device under test, which is then measured by the Vector Network Analyzer receivers on the other side.
Reflection measurement measures the signal that travels back towards the source due to reflections(2).
The image(2) seen below further illustrates this concept.
Sources[edit]
(1)https://www.tek.com/vna/ttr500 - Tektronix
(2)https://www.tek.com/document/primer/what-vector-network-analyzer-and-how-does-it-work - Tektronix