Current sensor transfer impedance determination method: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
So: | So: | ||
<math>Imp.=-27,96-0.00+33.98=6,02 | <math>Imp.=-27,96-0.00+33.98=6,02 dBOhm</math> | ||
<math>Imp.\approx 2 \ Ohm</math> | |||
{{note|This method is not a replacement for a real calibration.}} | {{note|This method is not a replacement for a real calibration.}} | ||
Revision as of 15:47, 23 January 2009
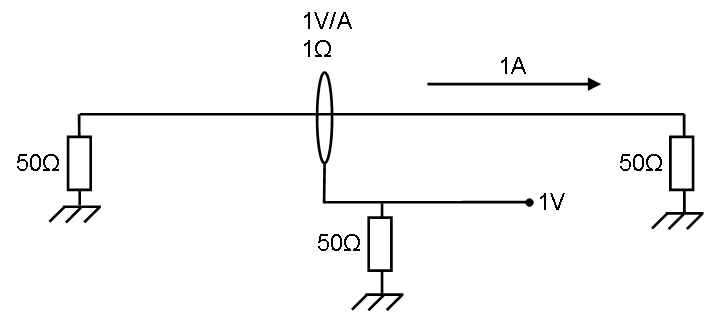
Theory[edit]
The left impedance is the signal generator which is generating enough power for 1 ampere.
This 1Amp. generates in the right impedance.
The current sensor has 1 ohm transfer impedance, this means 1 ampere generates 1 Volt on the measuring part below.
The power in the lower 50 ohm impedance is
So 1 ohm:
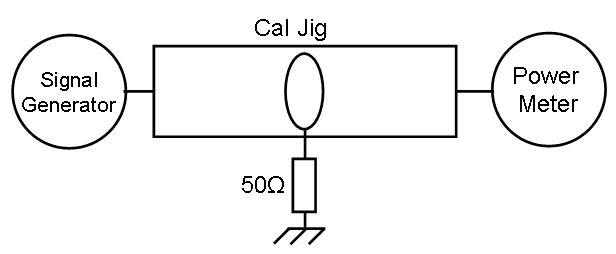
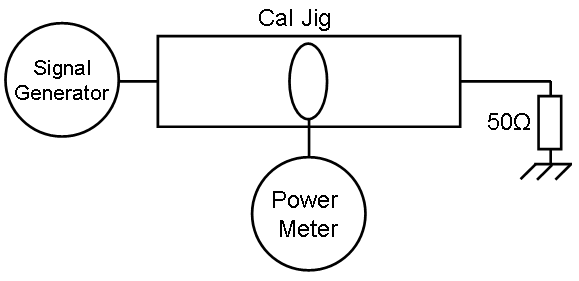
Reference measurement[edit]
Probe measurement[edit]
Calculation[edit]
and in dBm.
Example[edit]
On 10 MHz we have the following information:
- Calibration: 0 dBm.
- Measurement: -27,96 dBm.
So:
| Note: | This method is not a replacement for a real calibration. |