How to perform an ISO 11452-4 BCI (Bulk Current Injection) test[edit]
This application note explains how the ISO 11452-4 BCI (Bulk Current Injection) test can be performed with RadiMation®.
The ISO 11452-4 standard is used to test the immunity of automotive electronic components to conducted RF (radio frequency) disturbances injected into the wiring harness. The test frequency typically ranges from 1 MHz to 400 MHz, using both continuous and amplitude-modulated signals. The test ensures that the electronic devices can withstand the RF disturbances without performance degradation or failure.
The exact requirements and test methods for the BCI test are specified in the ISO 11452-4.
Necessary equipment[edit]
The following devices are required to run the calibration, verification, and EUT (Equipment Under Test) test:
- Signal generator
- Amplifier
- Coupler
- Forward power meter
- Current sensor
- Sensor power meter / Analyser
- 50 Ohm load
- 50 Ohm attenuator
- Current injection device
- Current injection calibration jig
- Cable drivers with corrections

|
Note:
|
If the current unit is shown as μA, it can be changed to dBμA by clicking Units, select Current and click Edit to change this.
|
Define the test level[edit]
The ISO 11452-4 BCI test requires test levels to be defined for different frequency ranges. The test level may vary depending on the application class or specific test plan, and these limits are set up as a correction file in RadiMation®.
-
 File
File
-
 New
New
-
 Correction
Correction
First, create a correction file in RadiMation® and specify the applicable test level for the BCI test based on the test requirements. The levels are typically specified in terms of current in dBμA for different frequency bands (see 'ISO 11452-4 BCI test level limits').
Ensure that the correction file has a Frequency column and a Current column with the unit set to dBμA.
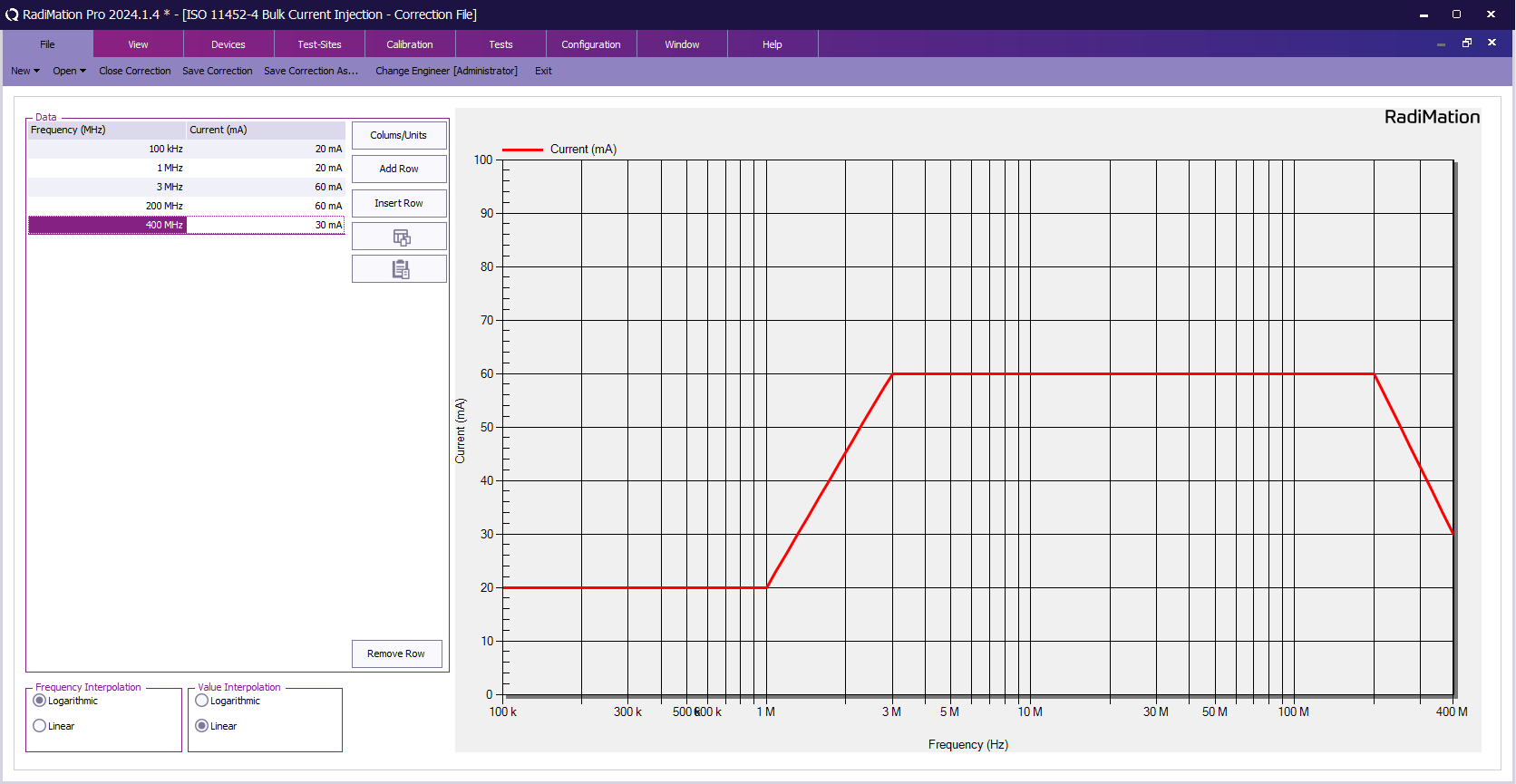
-
 File
File
-
 Save correction Save the test level as a correction file on disk.
Save correction Save the test level as a correction file on disk.
This correction file will be used during the calibration, verification, and EUT testing.
Calibration procedure[edit]
The calibration procedure is necessary to characterize losses in the setup and determine the correct power level for injection.
Calibration equipment[edit]
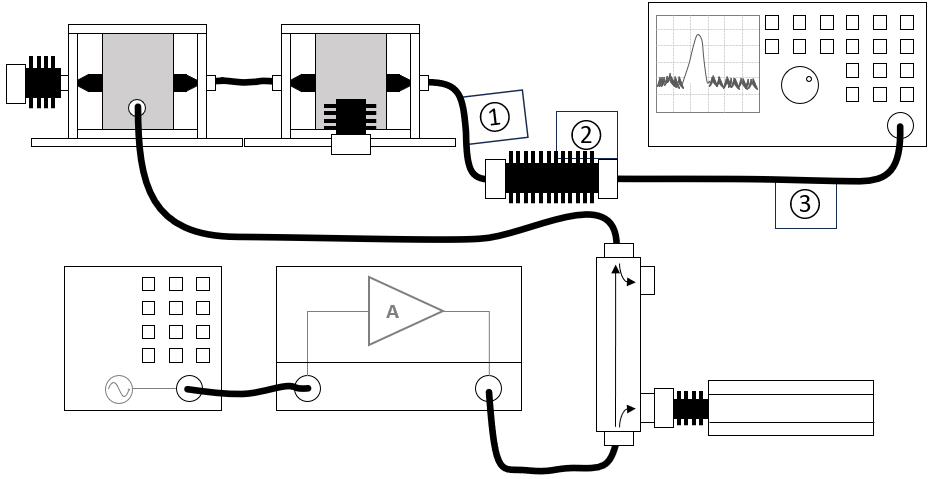
The configuration of the calibration test setup should include the following equipment:
| # |
Device name |
Tab in test site configuration window |
note
|
|
Signal Generator |
Devices 1 |
The signal generator to use
|
|
Amplifier |
Devices 1 |
The amplifier to use
|
|
Coupler |
Devices 1 |
The directional coupler to use
|
|
Forward power meter |
Devices 1 |
The forward power sensor to use
|
|
Power meter |
Devices 2 |
The power meter or analyzer for measuring current
|
|
Current probe |
Devices 2 |
The current monitoring probe used with a transfer factor applied
|
|
Injection clamp |
Devices 2 |
The bulk current injection (BCI) clamp
|
|
Calibration jig |
Devices 2 |
The jig used for the current injection calibration
|
| Cables
|
| ① |
Cable from current probe to power meter |
Cables |
Cable with a correction file specified for cable loss
|
| ② |
Cable from signal generator to injection clamp |
Cables |
Cable with specified loss of the used attenuator
|
| ③ |
Cable from injection clamp to current probe |
Cables |
Cable with a correction file specified for cable loss
|
Configure the calibration[edit]
The BCI test covers three primary frequency bands. The following settings can be configured according to ISO 11452-4 requirements:
| Band |
Frequency range |
Step size
|
| Band 1 |
1 MHz - 30 MHz |
1 %
|
| Band 2 |
30 MHz - 200 MHz |
1 %
|
| Band 3 |
200 MHz - 400 MHz |
0.5 %
|
These three bands should be calibrated individually. Calibration can be started by selecting:
-
 Calibration
Calibration
-
 System calibration
System calibration
-
 Conducted immunity
Conducted immunity
This example shows the configuration for Band 1; similar configurations can be created for the other bands.

 Start Start
|
The start frequency of the calibration (e.g., 1 MHz).
|
 End End
|
The stop frequency of the calibration (e.g., 30 MHz).
|
 Step Step
|
The frequency step, in this case, 1%.
|
 Test level Test level
|
The test level, in this case current.
|
 Variable Variable
|
The variable test level, select the correction file created earlier.
|
 Tolerance Tolerance
|
The regulation tolerance.
|
 Calibration method Calibration method
|
The power measurement that should result from the calibration: Forward power.
|
 Test equipment Test equipment
|
The calibration test equipment.
|
 Test engineer Test engineer
|
The engineer performing the calibration.
|
Calibration result[edit]
Once calibration is complete, the engineer will save the results in a calibration (.CAL) file. A separate calibration file will be generated for each frequency band.
EUT Testing[edit]
EUT Testing equipment[edit]
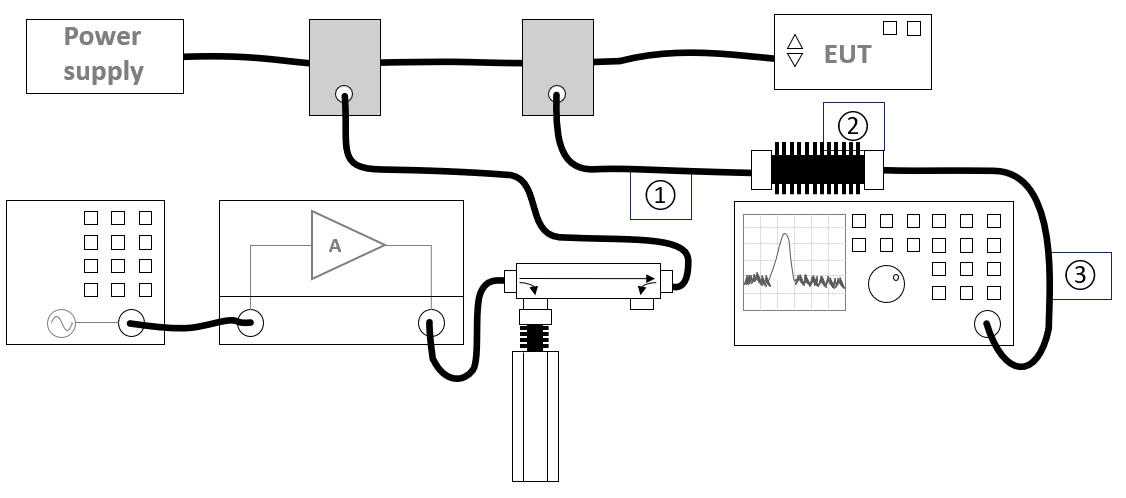
The configuration for EUT testing should contain the following devices:
| # |
Device name |
Tab in test site configuration window |
note
|
|
Signal Generator |
Devices 1 |
The signal generator to use
|
|
Amplifier |
Devices 1 |
The amplifier to use
|
|
Coupler |
Devices 1 |
The coupler to use
|
|
Forward power meter |
Devices 1 |
The forward power sensor
|
|
Power meter |
Devices 2 |
The analyzer for measuring current
|
|
Current probe |
Devices 2 |
The current probe with transfer factor applied
|
|
Injection clamp |
Devices 2 |
The bulk current injection clamp
|
Configure the EUT test[edit]
To perform the EUT test, configure the conducted immunity multiband test by selecting from the menu:
-
 Tests
Tests
-
 Conducted Immunity
Conducted Immunity
-
 Multiband
Multiband
The following bands should be configured:
| Band |
Frequency range |
Step size
|
| Band 1 |
1 MHz - 30 MHz |
1 %
|
| Band 2 |
30 MHz - 200 MHz |
1 %
|
| Band 3 |
200 MHz - 400 MHz |
0.5 %
|
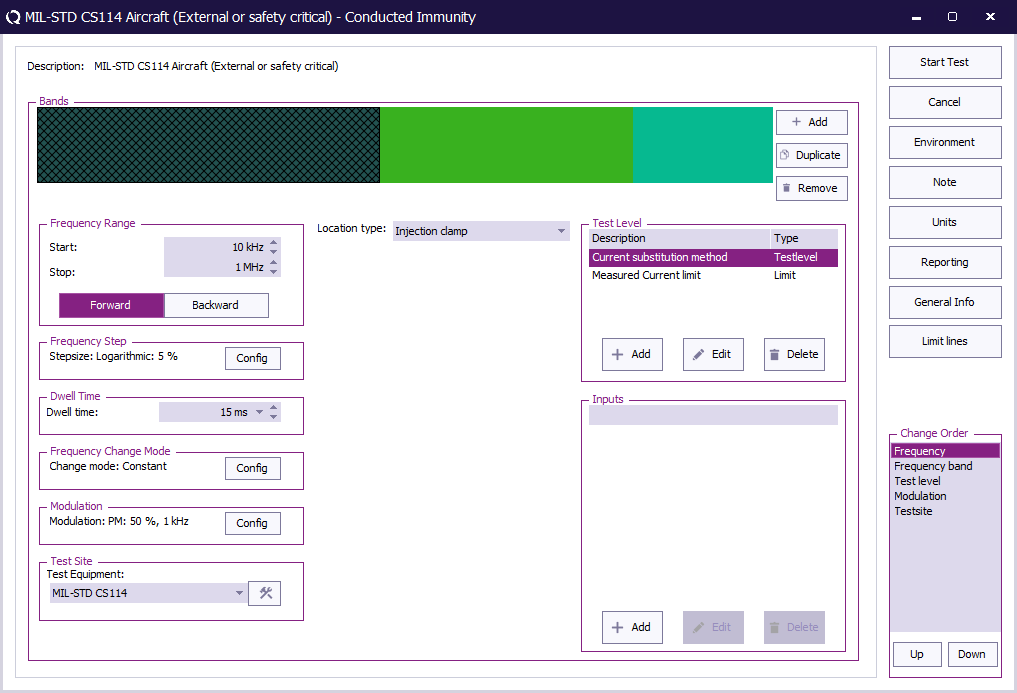
 Start Start
|
The start frequency of the test. For example 10 kHz.
|
 End End
|
The stop frequency of the test. For example 1 MHz.
|
 Frequency Step Frequency Step
|
The frequency step, see Table III.
|
 Dwell Time Dwell Time
|
The dwell time.
|
 Frequency Change Mode Frequency Change Mode
|
Constant.
|
 Modulation Modulation
|
Configure Pulse Modulation with 1 kHz and 50% duty cycle.
|
 Test equipment Test equipment
|
The equipment needed for the conducted immunity test.
|
 Location Type Location Type
|
Injection clamp.
|
 Test Level Test Level
|
Specify the current substitution method. Also add a "Measured Current Limit"
|
 Inputs Inputs
|
No inputs are needed.
|
To configure the pulse modulation settings click Config next to the modulation settings, click the PM tab, and enter the pulse modulation settings as specified in ISO 11452-4.
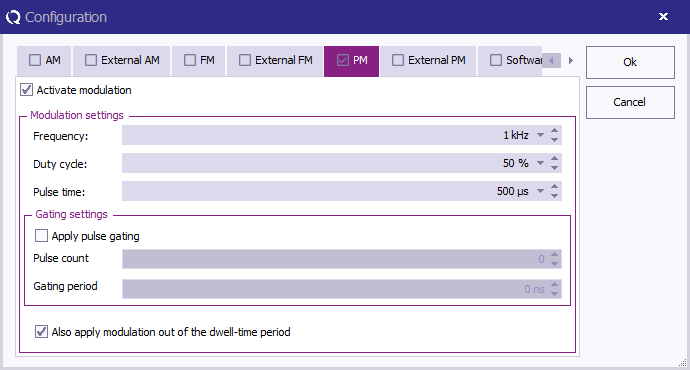
 Activate modulation Activate modulation
|
Check this checkbox to enable the pulse modulation.
|
 Frequency Frequency
|
The PM frequency 1 kHz.
|
 Duty Cycle Duty Cycle
|
A duty cycle of 50%.
|
 Also apply modulation out of the dwell-time period Also apply modulation out of the dwell-time period
|
Check this checkbox to enable modulation outside the dwell-time.
|
At TestLevel click Add to add a new Test level and select TestLevel - Current substitution method
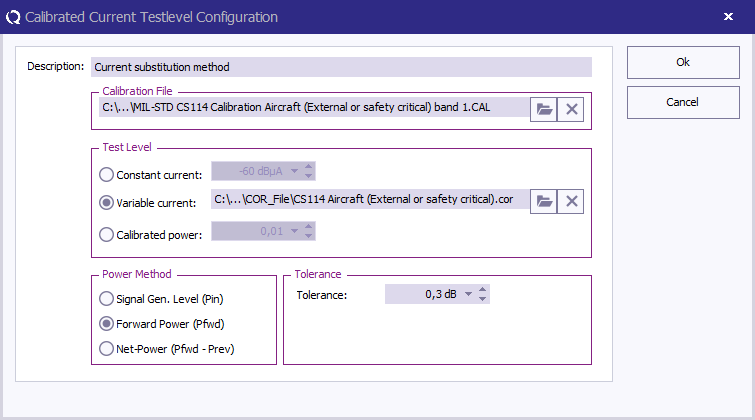
 Description Description
|
The description of the test level.
|
 Calibration file Calibration file
|
Select the calibration file to use for this band.
|
 Test level Test level
|
Variable current, and specify the correction file for the applicable test level.
|
 Calibration method Calibration method
|
Select Forward Power.
|
 Tolerance Tolerance
|
Specify the tolerance to use.
|
When all bands are configured press Start Test to run the EUT test.
EUT Test Result[edit]
Once the test is complete, the results are stored in a .LOG file. The test results can be reviewed by selecting the corresponding test from the list and clicking Info.
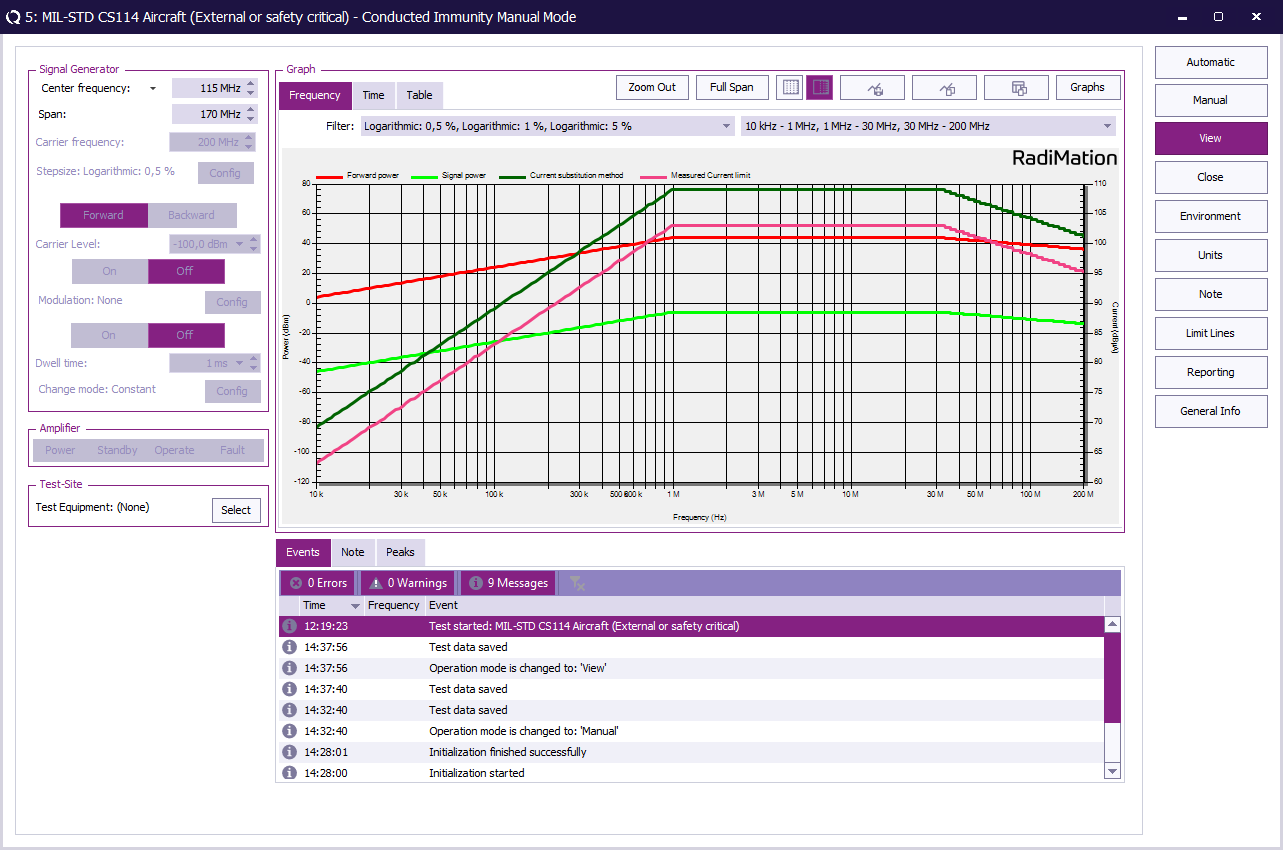
Conclusion[edit]
Using RadiMation®, you can effectively perform the ISO 11452-4 BCI test, ensuring compliance with automotive RF immunity standards and ensuring product robustness in the presence of RF interference.
[[Category
Application Note]]
 File
File
 New
New
 Correction
Correction  File
File
 Save correction Save the test level as a correction file on disk.
Save correction Save the test level as a correction file on disk. Calibration
Calibration
 System calibration
System calibration
 Conducted immunity
Conducted immunity  Tests
Tests
 Conducted Immunity
Conducted Immunity
 Multiband
Multiband 





